Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Molar Specific Heat Capacities in Terms of Gas Constant,Molar Specific Heat Capacity at Constant Volume,Mayer's Relation etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
A heater melts ice in a bucket completely into water in minutes and then evaporates all that water into steam in minutes sec. If latent heat of fusion of ice is , latent heat of steam will be (specific heat of water is )?
A metal cube absorbs of heat when its temperature is raised by . If the specific heat of the metal is , then the mass of the cube is
An immersion heater is rated . It should heat litre of water from to in about. (Specific heat of water is , density of water is )
The volume of moles of an ideal gas with degree of freedom is varied according to the law where is a constant. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure is
For the process to occur under adiabatic conditions, the correct condition is:
If of heat is supplied to gas at a pressure of , its volume increases from to . Calculate the change in its internal energy.
A diatomic gas expands from to as shown in the P-V graph. For this process choose the correct statement
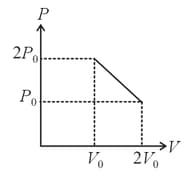
The piston is massless and the spring is ideal and initially streched the piston cylinder arrangement encloses an ideal gas. If the gas is heated quasistatically the graph.
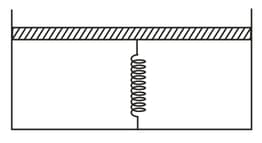
An ideal diatomic gas of moles and with initial pressure and volume undergoes a thermodynamic process. In this process the pressure is directly proportional to volume and the rms speed of the molecules is doubled. Then, the amount of heat required in this process is
At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is always greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
Molar specific heat at constant pressure is related to internal energy and absolute temperature as ________
and are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. It is observed that, for hydrogen gas and for nitrogen gas. The correct relation between and is:
Assertion: The specific heat at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat at constant volume i.e., .
Reason: In case of specific heat at constant volume, the whole of heat supplied is used to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas through while in case of specific of heat at constant pressure, heat is to be supplied not only for heating 1 mole of gas through but also for doing work during expansion of the gas.
If and denote the specific heats of nitrogen gas per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively, then
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of mass of water through is called its
One gram mole of an ideal gas with the ratio of constant pressure and constant volume specific heats is mixed with gram moles of another ideal gas with . If the for the mixture is , then what will be the value of ?
Specific heat of an ideal gas at constant volume and at constant pressure are related to universal gas constant are as
One mole of an ideal gas is heated at constant pressure through work done by the gas is
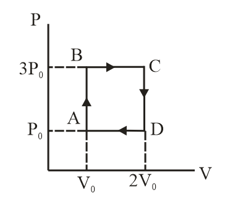
An ideal monatomic gas is carried along the cycle as shown in the figure. The total heat absorbed in this process is
A copper wire long is stretched by . If the energy stored in the stretched wire is converted to heat, calculate the rise in temperature of the wire. (Given: , Density of copper and Specific heat of copper
